We have discussed several different ways in which bitcoin creates an intrinsic value for itself. We also have discussed the absolute value that cryptography offers, and how States conjure up fiat money through legal violence via valor impositus, rather than creating money with real bonitas intrinseca value of metals that are coined. Now that we have an understanding of the above concepts, we can discuss how bitcoin is a commodity money, made from rare unique bits of data that create the whole cohesive framework that makes up bitcoin.
Satoshium
 For this post I am going to pretend that bitcoins are real coins that are minted from a new metal called Satoshium. This metal is ugly, has few uses, and cannot be physically touched, as it is invisible–overall it is pretty useless. However this new metal is very, very divisible, malleable and it can be transported over any digital communication channel. All Satoshium that will ever comes into existence is created through the coinbase reward that ‘mints’ bitcoin units, which happens during the process of ‘bitcoin mining’.
For this post I am going to pretend that bitcoins are real coins that are minted from a new metal called Satoshium. This metal is ugly, has few uses, and cannot be physically touched, as it is invisible–overall it is pretty useless. However this new metal is very, very divisible, malleable and it can be transported over any digital communication channel. All Satoshium that will ever comes into existence is created through the coinbase reward that ‘mints’ bitcoin units, which happens during the process of ‘bitcoin mining’.
The reason for the fictionalizing this alloy Satoshium is several fold:
1) To elaborate on the very important distinction between the legal creation of currency out of nothing, and how that is different from the minting of coins which must gain their value from the material the coins are made from. This is the distinction of legal tender under the force of law (valor impositus) and the nominal value states creates out of thin air (the expansion of the money supply), verses natural (bonitas intrinseca) money, which derives its value from no enforcement, or organization of men; but from the intrinsic use-value the object possess in-itself. This is seen most frequently with precious metals, but also with objects of use value like cigarettes.
2) Bitcoins can be used for much more than just money. When bitcoin units are creatively destroyed (proof-of-burn, colored coins, etc) it is similar to the melting down coins to use the metal for something more useful. Contracts, identity, transparent taxation, autonomous agents, etc. can all be created from Satoshium, or the outright destruction of bitcoin units.
3) Bitcoin is really a several dynamic systems working together (payment, identity, proof-of-existence, ownership, PGP system, etc) each with their own purpose. This is in addition to the fact that ‘bitcoins’–what one could think of as the cassacious coin, and I refer to as ‘bitcoin units’–is separate from owning a bitcoin address with no money in it.
Today we shall cover only the first item, and discuss how the bits of data that create the individual bitcoins have their own unique values that are not found within in the laws of men, but the laws of math.
Satoshium Mining
bitcoin monetary base
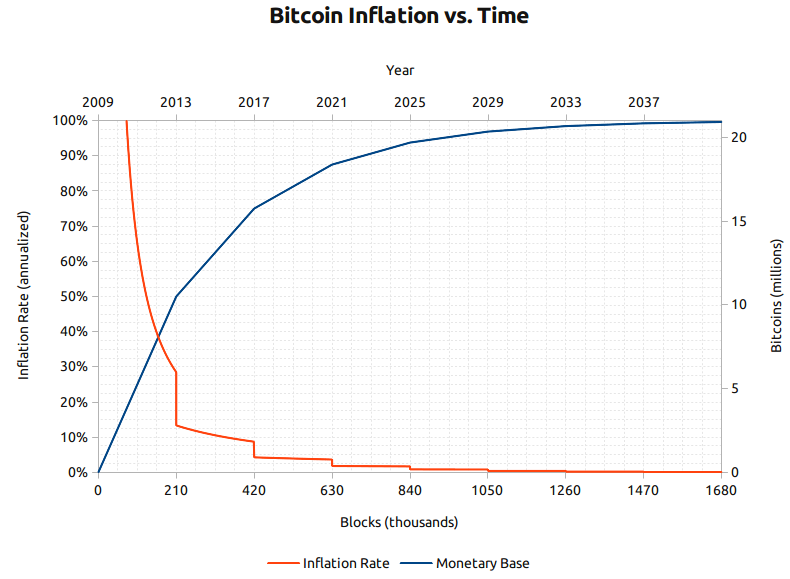
Let us think of Satoshium similar to gold or silver, with a few notable exceptions. Satoshium is rarer than gold; with only 2,100 trillion units (0.00000001 BTC–the smallest bitcoin unit, ‘a satoshi’) of Satoshium that can ever exist. Today there are about 1,350 trillion units of Satoshium that have been discovered through the ‘Satoshium mining’ process. More and more people are mining everyday with better, and better mining equipment–which is making it harder for current miners to find the mining reward. We will comeback to how bitcoins are ‘minted’ from satoshium using the coinbase reward process later in this post.
Another unique trait about satoshium is that it has a very, very steady inflation rate. For every 10 minutes of satoshium mining that is done on the bitcoin network (combining all of the mining power that everyone is using to find satoshium–be it 9 computers, or 9 billion) there are 5 billion units of satoshium discovered. After the first 4 years of mining, this amount was reduced by 1/2, to 2.5 billion units for the same 10 minute block of total work by the network. This amount will continue to divide in half every 4 years until there are no more units to be divided, which will be somewhere around 2138. Today there is much less satoshium available for mining than there was even just a few years ago–this is similar to the real deflation that metals, like gold, silver, and platinum experience over time, as they also have a finite supply.
Satoshium mining has become very difficult because so much mining energy is competing for these limited number of bitcoin units; the little guy can no longer mine satoshium on their own–it is simply too hard. This would be like trying to mine for gold with only a pick and shovel, while the guy next to you has a gold mining operation–you are not going to win. To resolve this, people discovered that if they ‘pool’ their work, everyone can share in the reward of satoshium mining based upon how much work they are doing for the bitcoin network.
The Minting of Bit-coins
 Satoshium is really the coinbase reward, which is the raw material that bitcoins are minted from (fun fact, the only way you can truly destroy a bitcoin is through not claiming the full coinbase reward). In the same manner that gold is just a hunk of metal before it is minted into a coin; so is satoshium is to bitcoin. When someone is rewarded for satoshium mining, those satoshium units are grouped into chunks of 100 million units and ‘minted’ single bitcoin. This is the coinbase reward process. This ‘mints’ satoshium units into bitcoins based upon what the block reward is at that time, and pays that reward of new coins out to a new bitcoin address. This is the ‘minting’ process and how the bitcoin network creates new bitcoins.
Satoshium is really the coinbase reward, which is the raw material that bitcoins are minted from (fun fact, the only way you can truly destroy a bitcoin is through not claiming the full coinbase reward). In the same manner that gold is just a hunk of metal before it is minted into a coin; so is satoshium is to bitcoin. When someone is rewarded for satoshium mining, those satoshium units are grouped into chunks of 100 million units and ‘minted’ single bitcoin. This is the coinbase reward process. This ‘mints’ satoshium units into bitcoins based upon what the block reward is at that time, and pays that reward of new coins out to a new bitcoin address. This is the ‘minting’ process and how the bitcoin network creates new bitcoins.
Though each bitcoin is created equally, the data that comprises of each individual bitcoin is unique and different. Each bitcoin addresses has unique identifying properties, that differentiate each individual bitcoin to their owners, but to no one else. This is similar to the serial number that is unique to each dollar bill. This means that the history of that particular bitcoin (or subdivisions of that bitcoin) can be tracked, and can only be spent when the 53-digit unique hexadecimal private key authorizes its movement. If properly secured, it is impossible to ‘hack’ a bitcoin address and take the money from that address; as only the private key will be able to move it. This is why there are several bitcoin addresses that have tens of millions of dollars in them, and not a single one has been hacked.
The mining process is also what ensures that there are no ‘double-spend’ attacks. In lay-terms, a double-spend attack is similar to check-kiting, where one spending the balance in checking account twice before the bank can check to make sure the funds are there. We won’t go into details about this right now, but just be aware that the mining process also acts as the gatekeepers to the transference of funds, and offers mathematical assurance that no coins can be stolen, or double-spent.
The Money Supply of Bitcoin
The reason for us fictionalizing the metal Satoshium is to make clear the distinction between fiat currency that are made from nothing, and commodity money which must derive their value from an object’s intrinsic worth–the value is found in the money itself, not vice-versa. A fiat currency is a scrips certificate of exchange issued from a central bank. The scrip itself (such as a $20 bill) is just worthless paper–there is no bonitas intrinseca about it. An infinite number of these scrips can be created, as their values are created and set by the dollar accounting system controlled by the Third Bank of the United States (also known as The Fed–a misleading term that I hate). Each one of these scrips can be redeemed for goods and services for the nominal value printed on it, because it is legal tender–one must accept fiat money in exchange for goods or services. If not, you will face the wrath of the law.
Historically, once could exchange the nominal value of these worthless papers for a precise measure of commodity money, such as gold or silver. However, fiat currency no longer has any sort of value backing them–since 1973 they have been free-floating. Governments are now free to print as much money as the like, which they are happily doing. This is because there has been a low level currency war going on since 2008, and it is starting to intensify. This means that while there still is a finite, natural supply of all physical objects; there now is twice as much money (in the case of the US) that can purchase those same objects.
This is how governments expand the money supply to create inflation. This bleeds the value of the hard-earned savings of common people, in order to further enrich the current ruling class. All people in all nations are now facing these political calamities that will make us all economic casualties.
Velocity of Money

Velocity of USD
When more units of a currency are injected into circulation, this causes for a total number of units within the system to increase. If the velocity of money were normal today, this would mean that the prices of everything would double over night–but it has not. This is because the velocity of money is at historic lows, at less than 1/2 of what it normally is. This is not a mistake, but a response to the QE of the FED.
Let us compare this to how bitcoins are ‘minted’. Bitcoins derive their value from the bonitas intrinseca, the real economic work that has been preformed in the Satoshium mining process, and the use-value that Satoshium has. Each and ever single bitcoin in existence must have came from a coinbase reward–there is no other way to create bitcoins. In order to create the coinbase reward, real computational work that takes real energy–no different from the energy used to dig gold from the ground–must be preformed.
With Satoshium mining, this ‘work’ is done in the form of solving very, very, very complex mathematic problems that secure the network from ever being corrupted. This gives each bitcoin unit equal, market-based value due to the fact that it cost real-time energy to produce bitcoin today. There is no way to modify the number of bitcoin units that can be created (unlike fiat money), as bitcoins can only come from the coinbase reward, and that is hardcoded into bitcoin. This ensures all bitcoiners that no one can ever just change the supply of bitcoin in the way the US can, or any other central bank can for their currency (I’m looking at you Japan and EU).
Bitcoin as a Currency

This is a public bitcoin address. If you have the private key for this address you can control the money there.
For us to understand bitcoin as a currency, let us think of bitcoin paper wallet for the moment. This is a piece of paper that has the private key of a bitcoin address printed on it. When one inputs the private key of that address into a bitcoin client, they can access, and transfer the bitcoin found in that addresses. This is a currency bill in the most fundamental sense of the word; as it is not that piece of paper that has any value, but what it represents. What has value is the private key, as that can access the bitcoin–not the paper itself. The paper has only exchange value, not use-value. This is how banking classically existed for centuries with banking bills representing some value of gold until the 1973, when the dollar dropped its peg to gold.
Although bitcoin is called a digital currency, that is a bit of a misnomer. Bitcoin is not a currency but a commodity-money. Bitcoins must come from the coinbase reward process, and that process can only be done through the electrical labor of mining. Thus, like physical coins, a bitcoin can only be created when the correct ‘bits’ are ‘minted’ into bitcoins. Bitcoins cannot just be created willy-nilly–real computational work must be done, and real energy expended to mint bitcoins.
This is why we have differentiated the creation of bitcoin units from that of Satoshium mining. If we are to mint coins, physical or otherwise, we must have something to mint, we cannot make coins from nothing! And this is the very place that commodity monies are different from fiat money–fiat money does not represent anything other than the law, whereas bitcoins ARE something–very special data sets verified by the bitcoin network.
Bitcoin is a Commodity Money
 Bitcoin is a commodity money because the cryptography that bitcoin is built on top of. This has created the contract that limits the supply of bitcoin units and protects the bitcoin payment network. It is cryptography that creates the immutable and fungibility of bitcoin units and the imperium of the bitcoin network. This immutability creates a use-value for bitcoin, which also creates its exchange value. Furthermore, the ‘satoshium’ units of bitcoin can be broken down and used for all sort of other various contractual functions. By understanding bitcoin as a commodity money, we can see the true value that bitcoin has is outside of the legal constructs of the state.
Bitcoin is a commodity money because the cryptography that bitcoin is built on top of. This has created the contract that limits the supply of bitcoin units and protects the bitcoin payment network. It is cryptography that creates the immutable and fungibility of bitcoin units and the imperium of the bitcoin network. This immutability creates a use-value for bitcoin, which also creates its exchange value. Furthermore, the ‘satoshium’ units of bitcoin can be broken down and used for all sort of other various contractual functions. By understanding bitcoin as a commodity money, we can see the true value that bitcoin has is outside of the legal constructs of the state.
The internet now has money that is loyal to no political body, or statist organizations; but to digital ideals alone. This is not just the economic base of a new epoch, but a political one as well. Bitcoin is the economic praxis that will allow for humans to create a new class consciousness. We can use the internet to help us create a new society, and we can use bitcoin as the economic mode to create that new world.
Bitcoin is not about money, and has nothing to do with money. Bitcoin is about political power, sovereignty, and the freedom of economic exchange. This is in direct and antagonistic relations to any and all states. Bitcoin seeks to destroy the old institutions of political power, and replace them with new digitized, decentralized ones.
Once people start to see and reject the corrupt and worthless scrips of the states, there is going to be a great unraveling unlike anything we have seen before. The crisis will collapse the value of all fiat money to becoming nearly worthless, and the value of cryptocurrencies will explode. There will be chaos, and there will be anarchy–but these are the conditions of creative destruction that we must have in order to rebuild something better in place of this corrupt and wicked system called state capitalism.
—
Next: Bitcoin and The History of Money


 For this post I am going to pretend that bitcoins are real coins that are minted from a new metal called Satoshium. This metal is ugly, has few uses, and cannot be physically touched, as it is invisible–overall it is pretty useless. However this new metal is very, very divisible, malleable and it can be transported over any digital communication channel. All Satoshium that will ever comes into existence is created through the coinbase reward that ‘mints’ bitcoin units, which happens during the process of ‘bitcoin mining’.
For this post I am going to pretend that bitcoins are real coins that are minted from a new metal called Satoshium. This metal is ugly, has few uses, and cannot be physically touched, as it is invisible–overall it is pretty useless. However this new metal is very, very divisible, malleable and it can be transported over any digital communication channel. All Satoshium that will ever comes into existence is created through the coinbase reward that ‘mints’ bitcoin units, which happens during the process of ‘bitcoin mining’.
 Satoshium is really the coinbase reward, which is the raw material that bitcoins are minted from (fun fact, the only way you can truly destroy a bitcoin is through not claiming the full coinbase reward). In the same manner that gold is just a hunk of metal before it is minted into a coin; so is satoshium is to bitcoin. When someone is rewarded for satoshium mining, those satoshium units are grouped into chunks of 100 million units and ‘minted’ single bitcoin. This is the coinbase reward process. This ‘mints’ satoshium units into bitcoins based upon what the block reward is at that time, and pays that reward of new coins out to a new bitcoin address. This is the ‘minting’ process and how the bitcoin network creates new bitcoins.
Satoshium is really the coinbase reward, which is the raw material that bitcoins are minted from (fun fact, the only way you can truly destroy a bitcoin is through not claiming the full coinbase reward). In the same manner that gold is just a hunk of metal before it is minted into a coin; so is satoshium is to bitcoin. When someone is rewarded for satoshium mining, those satoshium units are grouped into chunks of 100 million units and ‘minted’ single bitcoin. This is the coinbase reward process. This ‘mints’ satoshium units into bitcoins based upon what the block reward is at that time, and pays that reward of new coins out to a new bitcoin address. This is the ‘minting’ process and how the bitcoin network creates new bitcoins.

 Bitcoin is a commodity money because the cryptography that bitcoin is built on top of. This has created the contract that limits the supply of bitcoin units and protects the bitcoin payment network. It is cryptography that creates the immutable and fungibility of bitcoin units and the imperium of the bitcoin network. This immutability creates a use-value for bitcoin, which also creates its exchange value. Furthermore, the ‘satoshium’ units of bitcoin can be broken down and used for all sort of other various contractual functions. By understanding bitcoin as a commodity money, we can see the true value that bitcoin has is outside of the legal constructs of the state.
Bitcoin is a commodity money because the cryptography that bitcoin is built on top of. This has created the contract that limits the supply of bitcoin units and protects the bitcoin payment network. It is cryptography that creates the immutable and fungibility of bitcoin units and the imperium of the bitcoin network. This immutability creates a use-value for bitcoin, which also creates its exchange value. Furthermore, the ‘satoshium’ units of bitcoin can be broken down and used for all sort of other various contractual functions. By understanding bitcoin as a commodity money, we can see the true value that bitcoin has is outside of the legal constructs of the state.